Before we begin, a brief reminder: Medical Justice provides consultations to doctors facing medico-legal obstacles. We have solutions for patient conflicts, unwarranted demands for refunds, online defamation (patient review mischief) and meritless litigation. We also provide counsel specific to COVID-19. If you are navigating a medico-legal obstacle, request a consultation.
Tired of COVID-19? Me too.
Several surgeons recently authored a paper in the peer-reviewed Journal of Vascular Surgery. Prevalence of unprofessional social media content among young vascular surgeons.
The same article was presented at the Annual Symposium of the Society of Clinical Vascular Surgery.
The fastest and most reliable way to piss off a doctor is to call them unprofessional. The article has since been retracted and the authors apologized.
Details of the firestorm.
The authors intended to research whether vascular surgery trainees and recent graduates had public-facing social media accounts with content that could negatively affect their future reputations. Sounds benign enough. But the research failed to consider most of these doctors had not yet graduated and, predictably, did not have a professional web site, walling off their professional life from their personal life. Most doctors, over time, have two social media presences. Their public professional life and private life. Still, sometimes one bleeds over to the other. Most of the time, it’s of no import. Zilch. Nada.
What put the authors in a vat of boiling water was their loose definition of unprofessional content. They described “clearly unprofessional content” and “potentially unprofessional content.” Examples of clearly unprofessional content included HIPAA violations, intoxicated appearance, unlawful behavior, possession of drugs and drug paraphernalia, and uncensored profanity or offensive comments about colleagues / work / patients. Examples of potentially unprofessional conduct included holding/consuming alcohol, inappropriate attire., censored profanity, controversial political or religious comments, and controversial social topics. One of the “unprofessional” behaviors included in the study was “Inappropriate attire included pictures in underwear, provocative Halloween costumes, and provocative posing in bikinis/swimwear.”
For those interested in the statistical analysis:
There were 480 vascular surgeons identified. 325 (68%) were male, 456 (95%) held MD degrees, and 115 (24%) were integrated (0 + 5) vascular surgery residents. Of these, 235 had publicly identifiable social media accounts across all platforms. Sixty-one (26%) account holders had either clearly unprofessional or potentially unprofessional content. Eight accounts (3.4%) contained content categorized as clearly unprofessional: obvious alcohol intoxication in three Facebook accounts and uncensored profanity or offensive comments about colleagues/work/patients in one Facebook and five Twitter accounts. Potentially unprofessional content appeared in 58 accounts (25%) and included holding/consuming alcohol (29 accounts, 12.3%), controversial political comments (22 accounts, 9.4%), inappropriate/offensive attire (9 accounts, 3.8%), censored profanity (8 accounts, 3.4%), controversial social topics (6 accounts, 2.5%), and controversial religious comments (2 accounts, .9%). There was no significant difference in unprofessional content across sex, training paradigm (MD vs non-MD), or residency track (0 + 5 or 5 + 2; all P > .05). However, there was more unprofessional content for those who self-identified as vascular surgeons (33% vs 17%; P = .007).
And the conclusion. Drumroll, please.
One-half of recent and soon to be graduating vascular surgery trainees had an identifiable social media account with more than one-quarter of these containing unprofessional content. Account-holders who self-identified as vascular surgeons were more likely to be associated with unprofessional social media behavior. Young surgeons should be aware of the permanent public exposure of unprofessional content that can be accessed by peers, patients, and current/future employers.
The authors must have forgotten even doctors have real-world lives. Most, if not all, national specialty medical conventions sponsor an open bar during the welcome ceremony. It rarely leads to bedlam and debauchery. Doctors go to the pool, swim at the beach, have opinions, support political candidates, vote, go to church, eschew religion, celebrate Halloween, hate Halloween, and do lots of things that keep them from burning out. Good for them.
Once the arcane article was picked up by national media, the Twitter thunderstorm erupted. https://twitter.com/hashtag/MedBikini
Female doctors proudly described they will wear what they want when they want. And it has zero impact on whether they’re professional or not.
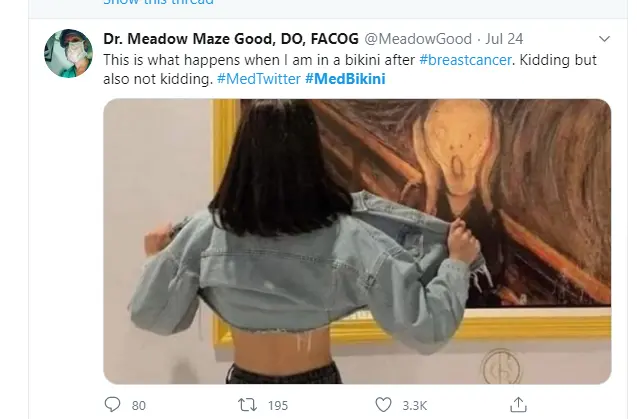

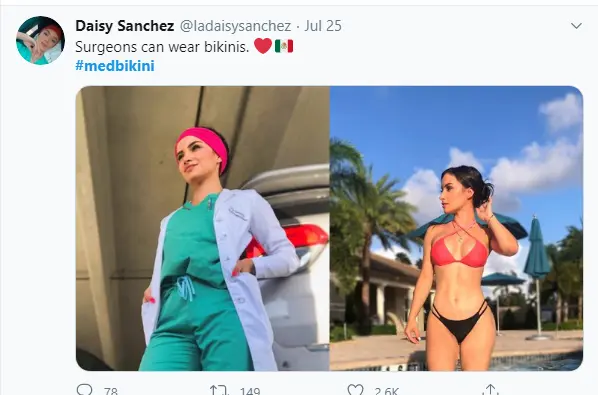
And, of course, solidarity from male colleagues.

Some surgeons also penned excellent scathing blog posts.
Other than the fact the research article was tone-deaf, does any of this matter?
Yes.
Boards of medicine are empowered to discipline physicians for so-called unprofessional behavior. Is unprofessional behavior defined by statute or regulation? Nope. It’s in the eye of the regulator. Discipline for unprofessional behavior can involve public reprimand, suspension, or revocation of one’s license. A harsh outcome. Can a doctor really lose her license for wearing a bikini? As an isolated event, probably not. But the better answer should be an unambiguous no.
Beyond the medical boards, can employers fire doctors for unprofessional conduct? Generally, yes. A private employer does not have to respect free speech rights. The government cannot shut you down for what you say (and even there, there are exceptions). Your employer can let you go. Every state other than Montana has “at-will” employment laws. That means the employer and the employee are each free to terminate the relationship. The only caveat is employers cannot fire a worker for discriminatory reasons. Discrimination may be based on race and sex. If an employer were to enforce off-hours dress codes, it would have to enforce it equally. No differentiation between men and women. Some states, such as California, Colorado, and New York make it difficult for employers to fire employees for behavior outside of work.
Doctors work hard. Doctors play hard. Most doctors wake up every day intending to do a great job for their patients. I doubt most patients fret if their doctor wears a bathing suit or has a beer. If these behaviors have no impact on patient care, patients should not care. My vote: The bar (no pun intended) for labeling some behavior as unprofessional should not be so low.
Enough of what I think. What do you think? Comment below.
PS: For those interested in the history of the bikini.
Clothing designer Louis Réard introduced his swimsuit in July 1946. He named it after the Bikini Atoll, where the first public test (Operation Crossroads) of a nuclear bomb had taken place only four days before. Purportedly, Réard—who hired a skywriter to advertise the new bikini as smaller than the world’s smallest bathing suit—claimed his version was sure to be as explosive as the U.S. military tests.
No runway model would wear it, so he hired a nude dancer from the Casino de Paris named Micheline Bernardini to model it at a review of swimsuit fashions.
A bathing suit qualified as a bikini, said Réard, only if it could be pulled through a wedding ring. He packaged the mere thirty squares inches of fabric inside a matchbox.
The Vatican formally decreed the design sinful, and several U.S. states banned its public use.
Medical Justice provides consultations to doctors facing medico-legal obstacles. We have solutions for patient conflicts, unwarranted demands for refunds, online defamation (patient review mischief) and meritless litigation. We also provide counsel specific to COVID-19. If you are navigating a medico-legal obstacle, request a consultation.
“Can Medical Justice solve my problem?” Click here to review recent consultations…
all. Here’s a sample of typical recent consultation discussions…
- Former employee stole patient list. Now a competitor…
- Patient suing doctor in small claims court…
- Just received board complaint…
- Allegations of sexual harassment by employee…
- Patient filed police complaint doctor inappropriately touched her…
- DEA showed up to my office…
- Patient “extorting” me. “Pay me or I’ll slam you online.”
- My carrier wants me to settle. My case is fully defensible…
- My patient is demanding an unwarranted refund…
- How do I safely terminate doctor-patient relationship?
- How to avoid reporting to Data Bank…
- I want my day in court. But don’t want to risk my nest egg…
- Hospital wants to fire me…
- Sham peer review inappropriately limiting privileges…
- Can I safely use stem cells in my practice?
- Patient’s results are not what was expected…
- Just received request for medical records from an attorney…
- Just received notice of intent to sue…
- Just received summons for meritless case…
- Safely responding to negative online reviews…
We challenge you to supply us with a medico-legal obstacle we haven’t seen before. Know you are in good hands. Schedule your consultation below.
Learn how Medical Justice can protect you from medico-legal mayhem…
Take Advantage of Our Review Monitoring Service
With eMerit, we help you automate review collection and posting to improve your online reputation.
Consult with a Medico-Legal Expert
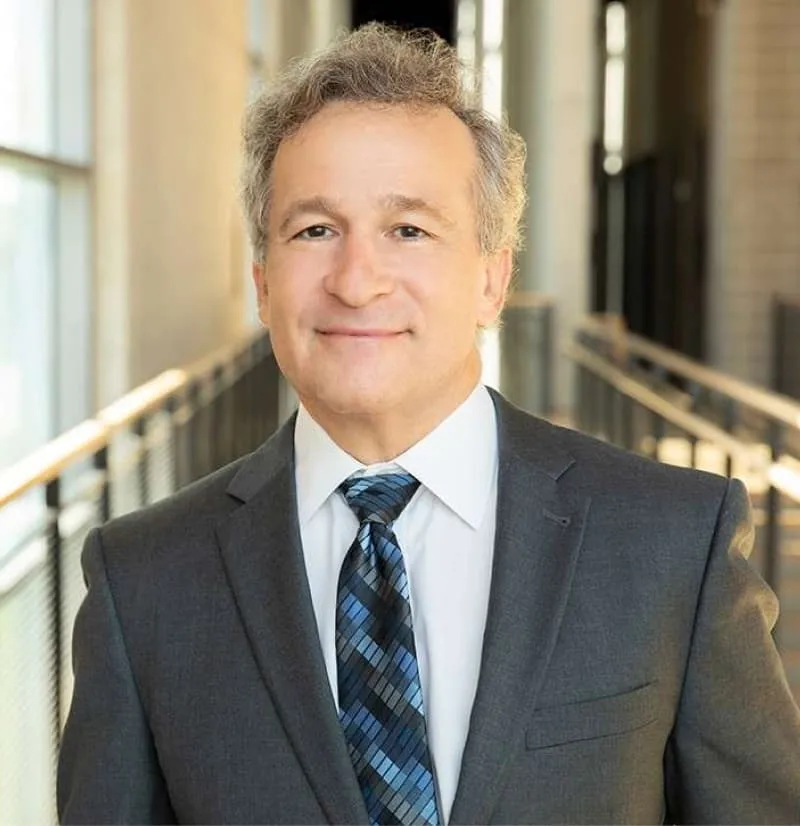
Medical Justice Founder and CEO, Jeff Segal, MD, JD and our expert team provide consultations to doctors in need of guidance.
Meet the Experts Driving Medical Justice
Our Executive Team walks with our member doctors until their medico-legal obstacles are resolved.
Jeffrey Segal, MD, JD
Chief Executive Officer and Founder
Dr. Jeffrey Segal, Chief Executive Officer and Founder of Medical Justice, is a board-certified neurosurgeon. Dr. Segal is a Fellow of the American College of Surgeons; the American College of Legal Medicine; and the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. He is also a member of the North American Spine Society. In the process of conceiving, funding, developing, and growing Medical Justice, Dr. Segal has established himself as one of the country’s leading authorities on medical malpractice issues, counterclaims, and internet-based assaults on reputation.
Dr. Segal was a practicing neurosurgeon for approximately ten years, during which time he also played an active role as a participant on various state-sanctioned medical review panels designed to decrease the incidence of meritless medical malpractice cases.
Dr. Segal holds a M.D. from Baylor College of Medicine, where he also completed a neurosurgical residency. Dr. Segal served as a Spinal Surgery Fellow at The University of South Florida Medical School. He is a member of Phi Beta Kappa as well as the AOA Medical Honor Society. Dr. Segal received his B.A. from the University of Texas and graduated with a J.D. from Concord Law School with highest honors.
In 2000, he co-founded and served as CEO of DarPharma, Inc, a biotechnology company in Chapel Hill, NC, focused on the discovery and development of first-of-class pharmaceuticals for neuropsychiatric disorders.
Dr. Segal is also a partner at Byrd Adatto, a national business and health care law firm. With decades of combined experience in serving doctors, dentists, and other providers, Byrd Adatto has a national pedigree to address most legal issues that arise in the business and practice of medicine.




As usual, great article. The Bikini was introduced the month before I was born, hence I have been a fan since birth.
I am sorry the authors felt they had to remove the article. I thought free speech was protected. I guess for only some of us.
Who were these prigs? [sic] I assume they’re at a university–or a monastery. Which one?
If they (who are they BTW?) want perfect physicians, they have to: 1-Triple our income (at least). 2-Stop Medicare audits. 3-Have insurance getting out of our lives; they should contract and negotiate directly with patients, NOT us. 4-Reduce the salary of hospital administrators to those of nurse managers and have them working for physicians, NOT the other way around. Until then, I will only let my GF render an opinion on my speedo.
In this day and age, the most egregious statistic is this one: “There were 480 vascular surgeons identified. 325 (68%) were male”. These authors would have been much better off gazing at their own navels to analyze why this is true and how they may have contributed to this problem rather than gazing upon those of doctors who actually have a life. It’s time to lead these doddering old farts out by their walkers and figure out how to address the systemic scotoma that doesn’t recognize this appallingly unfair discrepancy. These authors are proudly showing off their ignorance and distracting their readers with a poorly veiled puritanical perspective. The only valid response to this article is, “OK, Boomer. Time’s up.”
As a a general principle, doctors and other medical professionals should NOT be censured for what they do OUTSIDE of their professional roles.
What they do in their private lives is their own business. Doctors and other medical professionals should NOT be harassed on disciplined for wearing swimwear or expressing political views on social media outside of their professional capacity as health care providers.
Around a decade ago, while working as a medical doctor in a small Alabama military town, I was harassed by a former soldier and my employer pressured me as well after I was involved with the anti war movement and attended a large peaceful gathering outside a military base in the region.
At that time, although pressured and intimidated, I refused to stop my involvement in the anti war movement. The reason for that is that as a physician and as a human, I did not believe that my involvement in civic society and the anti war movement had any relevance whatsoever in my profession.
I did not believe that my employer had any right to tell me what I could do and could not do in my private life back then, and I do not believe employers have the right to do that now.
I have several thoughts when reviewing this article.
1) First and foremost, why in heaven’s name would a vascular surgery journal waste time or energy on this topic which has nothing to do with vascular surgery. Since they were snooping into personal twitter and other social media accounts they clearly had a lot of time on their hands to do that level of inspection and detective work. Are the author’s physicians or detectives?
2) I know that professionalism in media was starting to be drilled into me in the early to mid 1980s when I was in training. This carried over into social media. Adverse media could affect malpractice cases so physicians needed to have a certain level of circumspection.
3) In the 1990s I defended the then editor of the ASA newsletter when he called out in an editorial anesthesiologists going into the hospital in flip flops, cut off shorts, and with no medical garb in place (not even a stethoscope). Back in that day patients expected their physicians in hospital settings to at least make rounds in a white coat. The backlash was intense. But that was in a hospital setting. Social norms have changed today, but I still believe patients would like to see physicians in some type of professional attire. Most nurse practitioners and PAs have this down appearing in white coats etc. Physicians, not so much.
My surgical chief when I was an intern demanded that we change out of scrubs when leaving the OR into white coat, dress pants, dress shirt and a tie. The tie was omitted between memorial day and labor day due to the hospital not being air conditioned (1981).
4) There is a clear difference between professional web sites, and personal web sites, and professional social presence and personal social presence. Personal sites should be limited to friends and family for viewing purposes and not open to the general public. Invitations to patients for personal sites should be off limits in order to try to maintain some semblance of a professional – patient separation.
5) I would caution any physician or professional of any sort from posting pictures of drinking or drug related activity from social media, or even online due to the potential for a medical licensure board investigator to dig this stuff up and present it to the board for physician sanction. You have no idea how low these folks will sink to show how they are “policing the profession” to show how tough they are on physicians. Some board of medicine have quotas about how many physicians they have to take action against in a year in order to show the government that they are doing a good job of policing (read screwing over) physicians.
When your prior letters to the editor from years ago are dug up by an investigator to present you in a bad light and use your opinions against you, you must change your behavior to avoid being a target.
Big brother is out there and he is watching you. For that reason alone one must be vigilant in what posts online.
6) I started teaching the idea of being careful on social media to my children when they got to high school almost 20 years ago.
I pushed my son into deleting his facebook account when he was in HS, due to inappropriate content that he posted. He got back on social media later but the inappropriate postings or comments were nil at that point. He learned his lesson before the advent of cancel culture.
7) Cancel culture is alive and well on social media. There are trolls who exist simply to make other people’s lives miserable. They are the thought police or wish that they were. They can doxx users posting addresses and other personal information online simply because they took offense at a social media post. That is unfortunately the world we live in. I will post congratulations for birthdays and anniversaries, or benign comments about pets, but if anything is even slightly provocative, I will take it private or better still offline.
Why post anything that can come back and haunt you?
8) Keeping up a professional appearance on social media helps to avoid patients from coming on to you (male or female), and avoids getting you into a trap of alleged inappropriate behavior.
Some people are simply mentally ill and you do not wish to encourage them for any reason on social media so be careful.
9) Physicians are entitled to their own private lives, and are entitled to enjoy them.
But private lives should remain private and away from social media other than to immediate close friends and family. Interests in groups online is fine, but be mindful of comments.
In one group I made a comment about wooden sided subway cars from the late 1960s on a particular subway line, and received a hateful reply telling me that such a thing was not possible.
(Except it was because I rode on those cars). Subsequent later posts to that social media group by others documented those cars. But even such an innocuous comment about such a benign topic, brought out the worst in some poster.
To quote the beginning of Hill Street Blues TV show from decades ago “So be careful out there!”
We as physicians can never be too careful. As a professional, especially In healthcare, we are held to a higher standard. I believe the study authors had good intentions. There is a massive divide between those who grew up with the internet/social media and those of us who did not. I have chosen to never post anything that would knowingly cause even the most conservative individual to question my actions. I don’t feel the need to put my personal life up for viewing. Be careful. Haters love to hate….
Do we as physicians have a moral duty to conduct our private lives with a higher level of emotional control? The question is not whether to wear bikinis or if to have an alcoholic beverage. Our patients need to have confidence in our pursuit of moral foundations. Do we all fail in relationships at times? Of course, we do! Do our patients accept that we, too, have human frailties? They do, remarkably, they do. Do we attempt to see our failures and address them? Is the latter not the foundation of the sciences that drive medicine?
Social media is evil, and should be used for professional use only, if you’re a doctor – or any professional. All content posted to the internet should be considered like a tattoo, permanent and irremovable. In that regard, I advise anyone looking to pursue higher education to stay OFF the internet when it comes to social postings. The internet and social media may be helpful for one’s professional endeavors, and stains from personal posts should be avoided. I’ve been burned with a social post about our crappy school board in 2015 and was subsequently labeled a “racist”. Had I been wearing a Speedo, it may have gone over better. I’m a big proponent of the 1st Amendment, but in case you haven’t noticed, free speech is dead, and keeping a clean internet presence is paramount. Thank you.